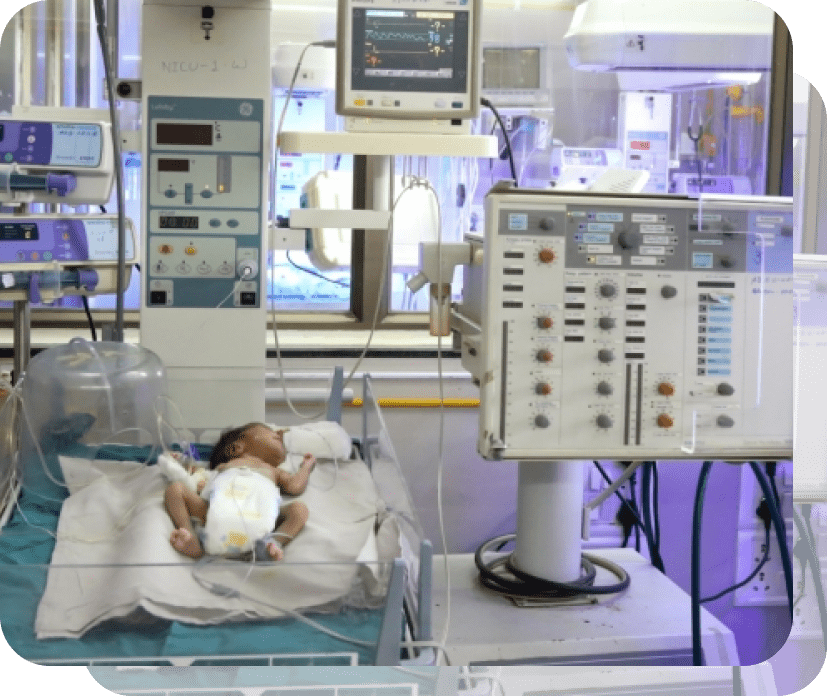
Newborn babies who need intensive medical attention are often admitted into a special area of the hospital called the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU). The NICU combines advanced technology and trained health care professionals to provide specialized care for the tiniest patients. NICUs may also have intermediate or continuing care areas for babies who are not as sick but do need specialized nursing care.
Some newborn babies will require care in a NICU, and giving birth to a sick or premature baby can be quite unexpected for any parent. Unfamiliar sights, sounds, and equipment in the NICU can be overwhelming. This information is provided to help you understand some of the problems of sick and premature babies. You will also find out about some of the procedures that may be needed for the care of your baby.
Most babies admitted to the NICU are premature (born before 37 weeks of pregnancy), have low birth weight (less than 5.5 pounds), or have a medical condition that requires special care. In the U.S., nearly half a million babies are born preterm, and many of these babies also have low birth weights. Twins, triplets, and other multiples often are admitted to the NICU, as they tend to be born earlier and smaller than single birth babies. Babies with medical conditions such as heart problems, infections, or birth defects are also cared for in the NICU.
These are some factors that can place a baby at high risk and increase the chances of being admitted to the NICU. However, each baby must be evaluated individually to determine the need for admission. High-risk factors include the following:
 Age younger than 16 or older than 40 years
Age younger than 16 or older than 40 years Drug or alcohol exposure
Drug or alcohol exposure Diabetes
Diabetes Hypertension (high blood pressure)
Hypertension (high blood pressure) Bleeding
Bleeding Sexually transmitted diseases
Sexually transmitted diseases Multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets, or more)
Multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets, or more) Too little or too much amniotic fluid
Too little or too much amniotic fluid Premature rupture of membranes (also called the amniotic sac or bag of waters)
Premature rupture of membranes (also called the amniotic sac or bag of waters)
 Fetal distress/birth asphyxia (changes in organ systems due to lack of oxygen)
Fetal distress/birth asphyxia (changes in organ systems due to lack of oxygen) Breech delivery presentation (buttocks delivered first) or other abnormal presentation
Breech delivery presentation (buttocks delivered first) or other abnormal presentation Meconium (the baby's first stool passed during pregnancy into the amniotic fluid)
Meconium (the baby's first stool passed during pregnancy into the amniotic fluid) Nuchal cord (cord around the baby's neck)
Nuchal cord (cord around the baby's neck) Forceps or cesarean delivery
Forceps or cesarean delivery Birth at gestational age less than 37 weeks or more than 42 weeks
Birth at gestational age less than 37 weeks or more than 42 weeks Birth weight less than 2,500 grams (5 pounds, 8 ounces) or over 4,000 grams (8 pounds, 13 ounces)
Birth weight less than 2,500 grams (5 pounds, 8 ounces) or over 4,000 grams (8 pounds, 13 ounces) Small for gestational age
Small for gestational age Medication or resuscitation in the delivery room
Medication or resuscitation in the delivery room Birth defects
Birth defects Respiratory distress including rapid breathing, grunting, or apnea (stopping breathing)
Respiratory distress including rapid breathing, grunting, or apnea (stopping breathing) Infection such as herpes, group B streptococcus, chlamydia
Infection such as herpes, group B streptococcus, chlamydia Seizures
Seizures Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) Need for extra oxygen or monitoring, intravenous (IV) therapy, or medications
Need for extra oxygen or monitoring, intravenous (IV) therapy, or medications Need for special treatment or procedures such as a blood transfusion
Need for special treatment or procedures such as a blood transfusion